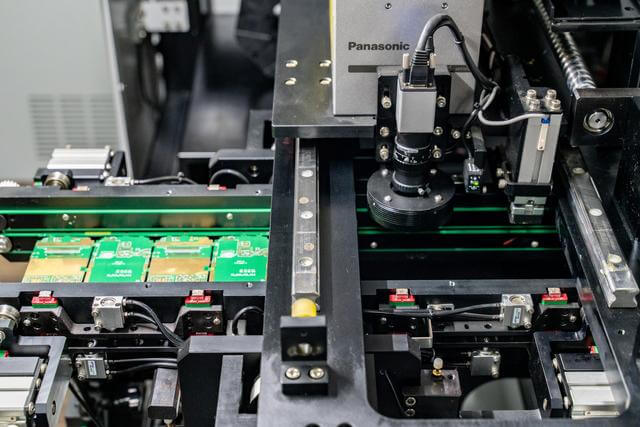
In PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) processing, flexible PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is more and more popular in electronic industry because of its unique flexible and thin characteristics. Flexible PCB is widely used in smart phones, wearable devices, medical devices and other fields. Although flexible PCB provides flexibility in design and spatial optimization, its manufacturing process faces some unique challenges. This paper will discuss the main challenges and solutions in flexible PCB processing to help manufacturers effectively deal with these problems and ensure high quality and reliability of products.
1.The main challenge of flexible PCB processing
1.1 material selection and processing
Flexible PCB is usually made of flexible materials such as polyimide (PI) , which are difficult to process. They require not only high-precision processing equipment, but also strict control of material processing to avoid material deformation or damage.
1.2 high-precision manufacturing
due to the special nature of flexible PCB, the manufacturing process requires high-precision equipment and processes. This includes accurate lamination, etching, and hole machining. Any small error can lead to circuit board dysfunction or failure.
1.3 welding technology
the welding process of flexible PCB is different from that of rigid PCB. Due to the elasticity of flexible PCB material, the traditional welding technology may lead to solder joint shedding or welding quality problems. Therefore, special welding technology for flexible materials is needed. 1.4 mechanical strength
flexible PCB need to maintain mechanical strength when bending or stretching to prevent damage to the circuit. High frequency bending and stretching may lead to break or fracture of circuit board, which requires that the strength and durability of the material be fully considered in the design and processing.
2、Solution
2.1optimize material selection
choose the suitable flexible PCB material. High quality polyimide (PI) materials are stable and reliable during processing. The use of materials from approved suppliers can reduce problems that may arise during processing. In addition, proper pre-treatment of materials, such as drying and cleaning, also helps to improve the quality of processing.
2.2Improve machining accuracy
improve the manufacturing accuracy of flexible PCB is to introduce advanced processing equipment and technology. Using high-precision laser etching technology and automatic laminating equipment can effectively control the manufacturing process of the error. In addition, the implementation of stringent quality control measures, including on-line monitoring and automated detection systems, can detect and correct problems in the process in a timely manner to ensure product consistency and stability.
2.3improved welding techniques
For the welding challenges of flexible PCB, special welding materials and processes can be used, such as low-temperature solder and accurate welding temperature control. These welding techniques can reduce the stress in the welding process, thus improving the reliability of the solder joint. In addition, pre-treatment before welding and post-welding inspection can also further ensure the quality of welding.
2.4mechanical strength enhancement
In the design stage, the mechanical strength of flexible PCB should be considered. For example, the durability of a circuit board can be improved by adding appropriate support structures and protective layers. In addition, the selection of materials with high elasticity, and avoid excessive bending and stretching during processing, also help to improve the mechanical strength and durability of flexible PCB.
2.5testing and verification
In the production process, regular testing and verification is an important measure to ensure the quality of flexible PCB. Potential problems can be identified and resolved by testing the electrical properties, mechanical strength and durability of the samples. Real-time monitoring with automatic test equipment can improve the test efficiency and accuracy and ensure the pass rate of each batch of products.

3、Application examples
3.1smart wearables
Smart wearable devices, such as smart watches and health monitors, use flexible pcbs to achieve lightweight and flexible designs. These devices require flexible PCB with good mechanical strength and stable electrical performance to ensure the reliability of equipment in daily use.
3.2medical devices
The flexible PCB used in medical devices is usually used for high-density circuit design and precise sensor layout. These applications require excellent durability and stability of flexible PCB to meet the stringent requirements of medical equipment.
3.3consumer electronics
In consumer electronics, flexible PCB can optimize the internal space and improve the flexibility of product design. For example, flexible pcbs can be used in the internal connection circuitry of smartphones to provide better structural design and functional integration.
Conclusion
Flexible PCB processing has become an important part of modern electronic products because of its unique design advantages and wide application. However, the process of its challenges, such as material processing, precision manufacturing, welding technology and mechanical strength problems, solutions are needed to optimize material selection, improve machining accuracy, improve welding technology, enhance mechanical strength, and periodically test and verify. By effectively solving these challenges, manufacturers can improve the quality and reliability of flexible PCB to meet the market demand for high-performance electronic products.